This post focuses on ACL’2024 papers, that are studying information extraction tasks.
Hypergraph based Understanding for Document Semantic Entity Recognition
Motivation
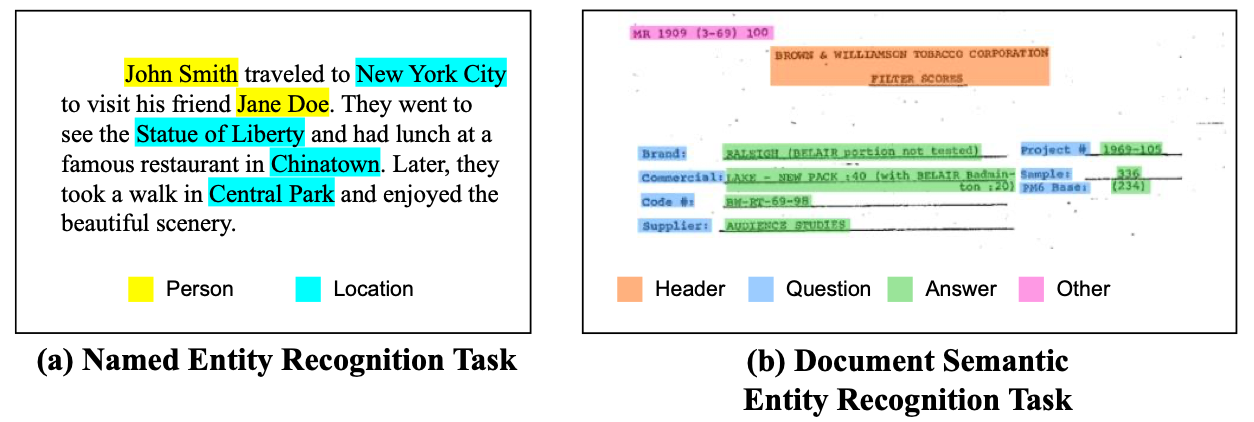 The researchers aimed to improve Semantic Entity Recognition (SER) by addressing both entity categories and boundary extraction, which existing models often overlook.
The researchers aimed to improve Semantic Entity Recognition (SER) by addressing both entity categories and boundary extraction, which existing models often overlook.
Method
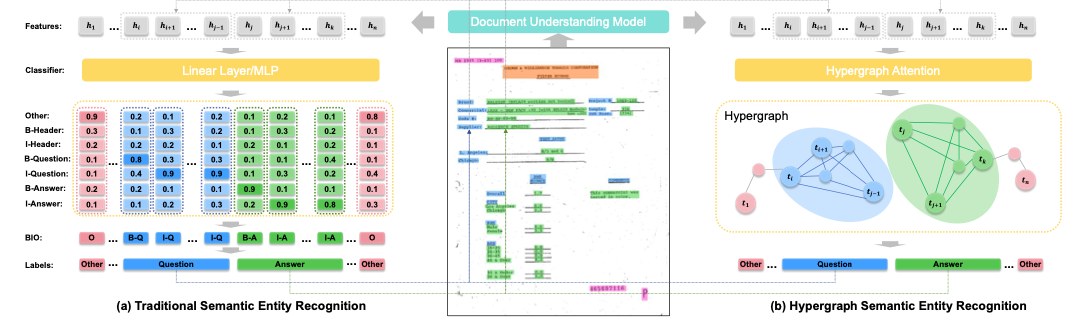
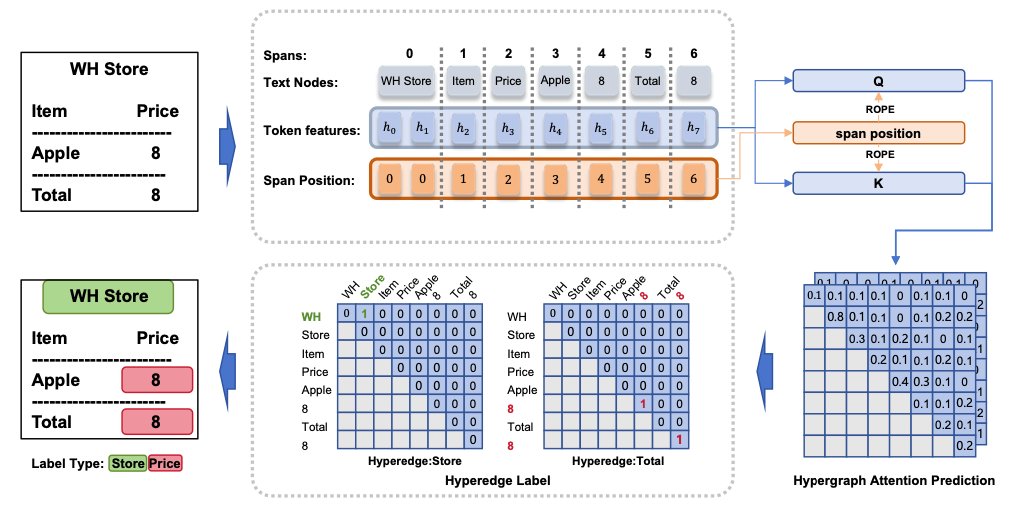 They introduced Hypergraph Attention (HGA) for SER, transforming the task into a hypergraph construction process to capture both entity categories and boundaries effectively.
They introduced Hypergraph Attention (HGA) for SER, transforming the task into a hypergraph construction process to capture both entity categories and boundaries effectively.
Results
The results of HGALayoutLM on FUNSD and XFUND reach the new state-of- the-art results.
Description Boosting for Zero-Shot Entity and Relation Classification
Motivation
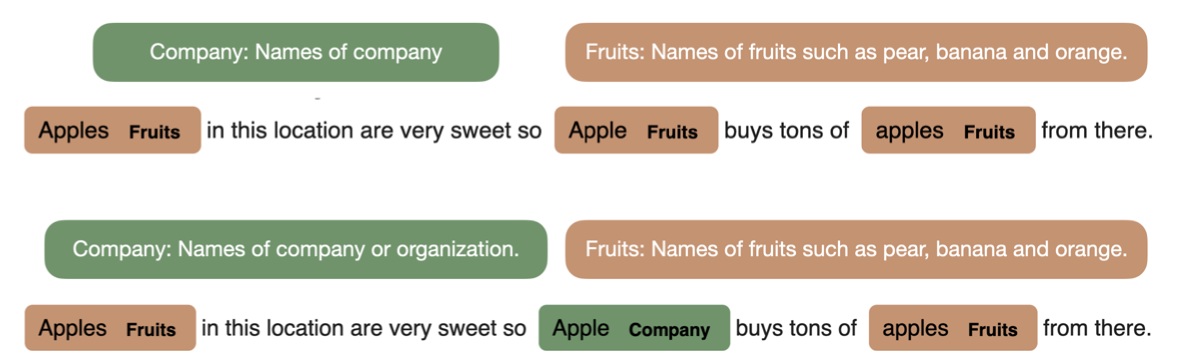 The researchers aimed to improve zero-shot entity and relation classification by addressing the problem of sensitivity to textual descriptions. Small changes in descriptions lead to inconsistent predictions, affecting model performance.
The researchers aimed to improve zero-shot entity and relation classification by addressing the problem of sensitivity to textual descriptions. Small changes in descriptions lead to inconsistent predictions, affecting model performance.
Method
They introduced UDEBO, a method that automatically generates and ranks different description versions using tools like paraphrasing, summarization, and language models to enhance zero-shot model accuracy.
Results
Proposed method outperform existing approaches and achieve new SOTA results on OntoNotesZS and FewRel datasets under the Zero-Shot Learning (ZSL) settings
Argument-Aware Approach To Event Linking
Motivation
 The researchers aimed to improve event linking, a task of connecting event mentions in text to knowledge base (KB) entries. Prior methods focused more on entity linking approaches and neglected the role of event arguments, making event linking less effective.
The researchers aimed to improve event linking, a task of connecting event mentions in text to knowledge base (KB) entries. Prior methods focused more on entity linking approaches and neglected the role of event arguments, making event linking less effective.
Method
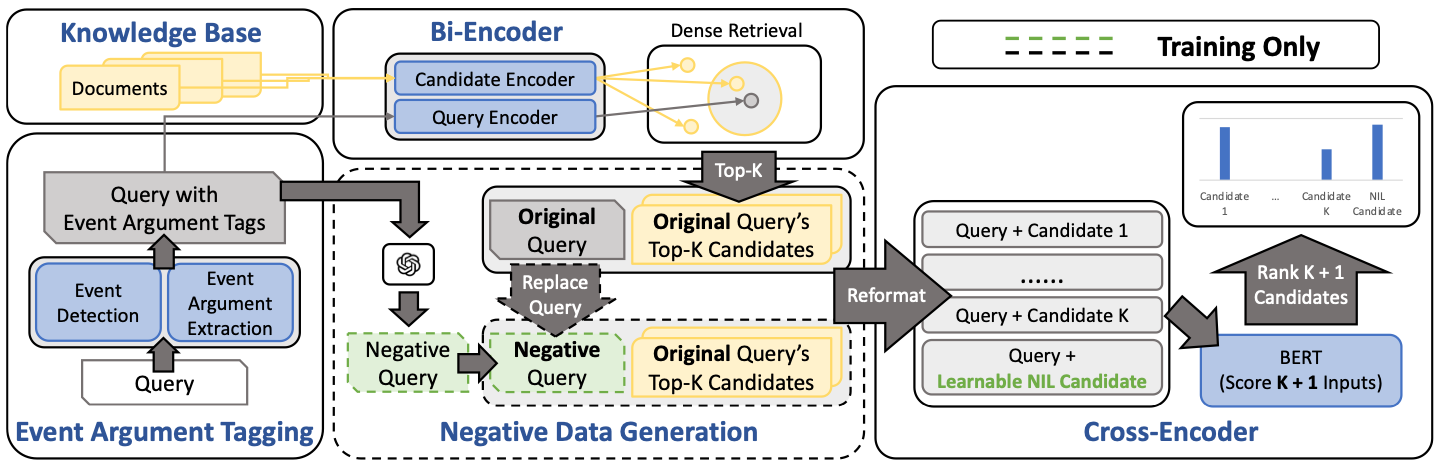 They introduced an argument-aware approach that uses event argument tagging to better identify and link events to KBs. Additionally, they created synthetic “out-of-KB” examples by manipulating event arguments to train the model for better handling events not found in the KB.
They introduced an argument-aware approach that uses event argument tagging to better identify and link events to KBs. Additionally, they created synthetic “out-of-KB” examples by manipulating event arguments to train the model for better handling events not found in the KB.
Results
Their approach improved both in-KB and out-of-KB performance, achieving a 22% accuracy boost in out-of-KB scenarios and over a 1% increase for in-KB event linking.
AlignRE: An Encoding and Semantic Alignment Approach for Zero-Shot Relation Extraction
Motivation
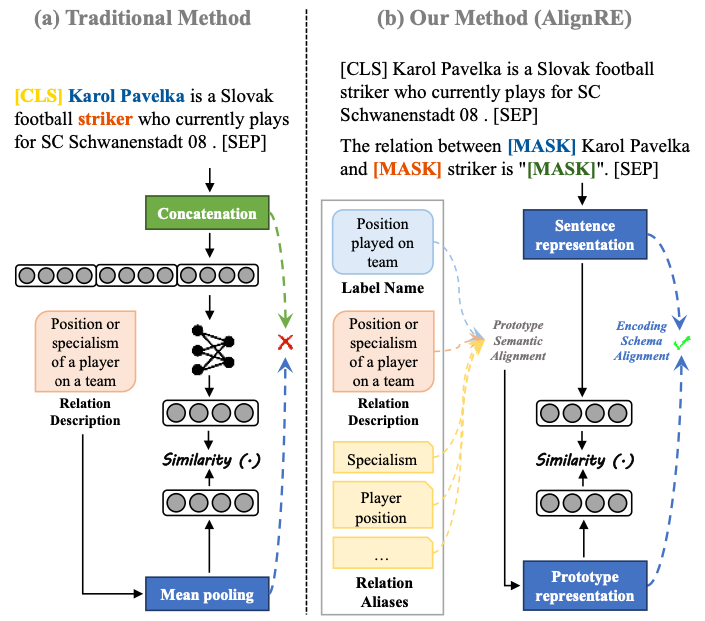 The researchers aimed to enhance Zero-Shot Relation Extraction (ZSRE), where existing methods fail due to the gap between encoding sentence embeddings and prototype embeddings. They wanted to address this gap and improve the quality of prototypes by utilizing more side information.
The researchers aimed to enhance Zero-Shot Relation Extraction (ZSRE), where existing methods fail due to the gap between encoding sentence embeddings and prototype embeddings. They wanted to address this gap and improve the quality of prototypes by utilizing more side information.
Method
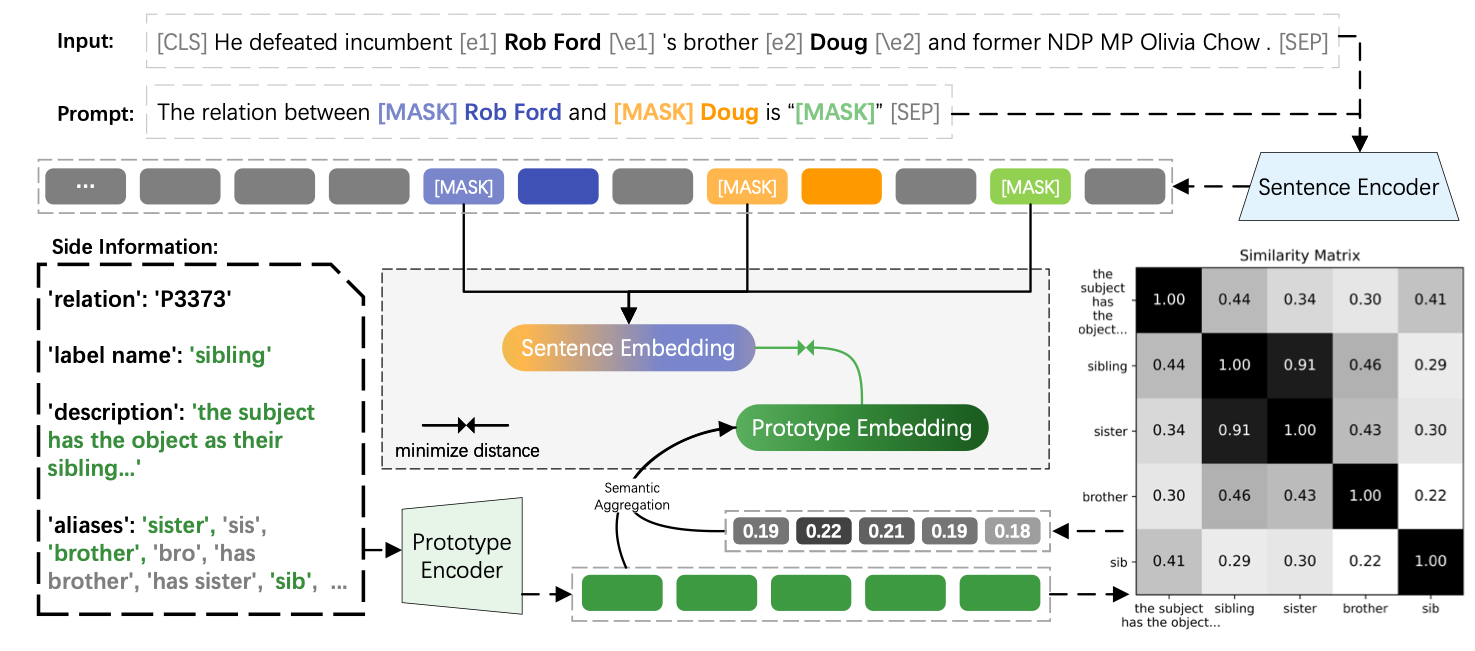 They proposed AlignRE, which uses encoding schema alignment and semantic alignment for relation extraction. This method introduces a prompt-tuning mechanism to align sentence and prototype embeddings and aggregates side information like labels and aliases to improve prototype quality.
They proposed AlignRE, which uses encoding schema alignment and semantic alignment for relation extraction. This method introduces a prompt-tuning mechanism to align sentence and prototype embeddings and aggregates side information like labels and aliases to improve prototype quality.
Results
AlignRE outperformed state-of-the-art models, improving F1 scores by 2.33 on FewRel and 1.47 on Wiki-ZSL, while also reducing manual effort and speeding up inference.
Statements: Universal Information Extraction from Tables with Large Language Models for ESG KPIs
Motivation
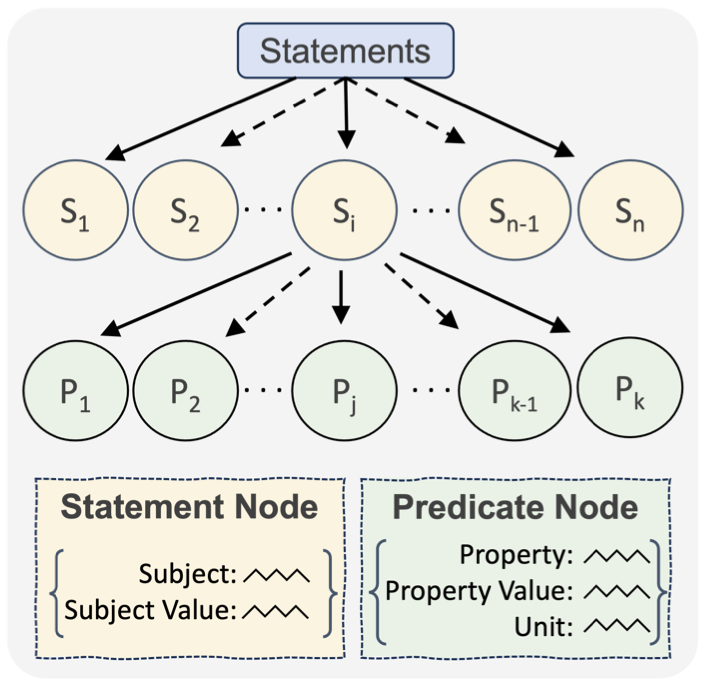 The researchers aimed to improve the process of extracting Environment, Social, and Governance (ESG) information from tables found in corporate reports. The task is challenging due to the wide variety of table structures used in these reports.
The researchers aimed to improve the process of extracting Environment, Social, and Governance (ESG) information from tables found in corporate reports. The task is challenging due to the wide variety of table structures used in these reports.
Method
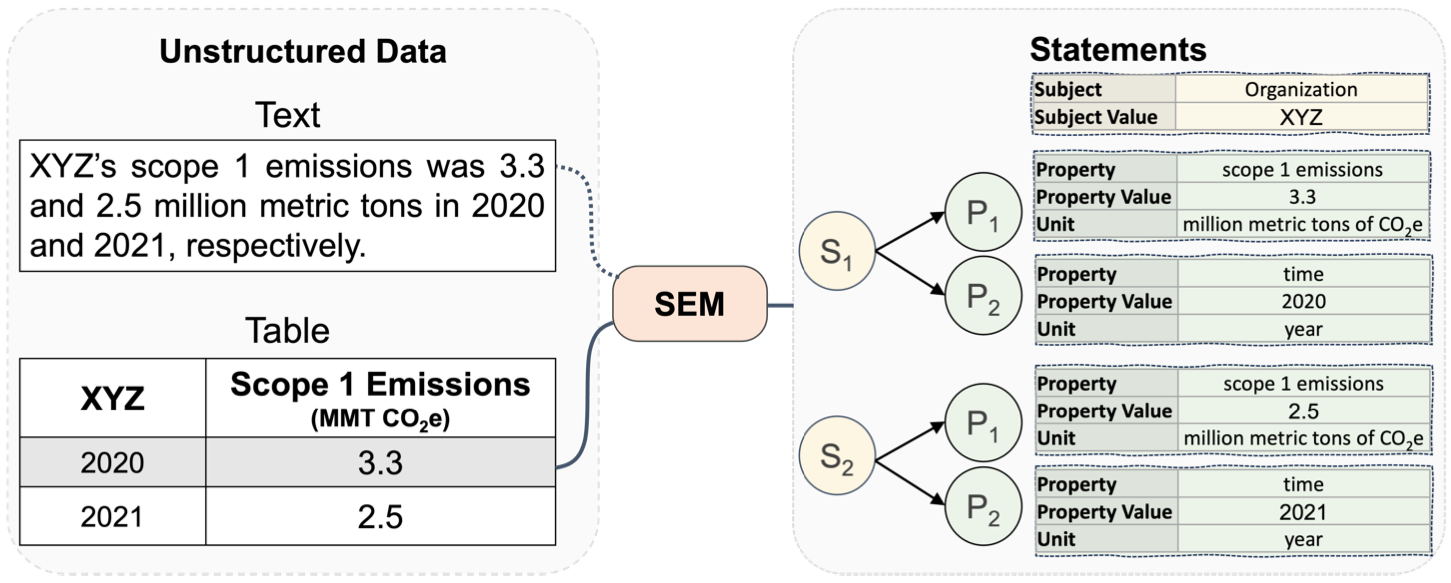
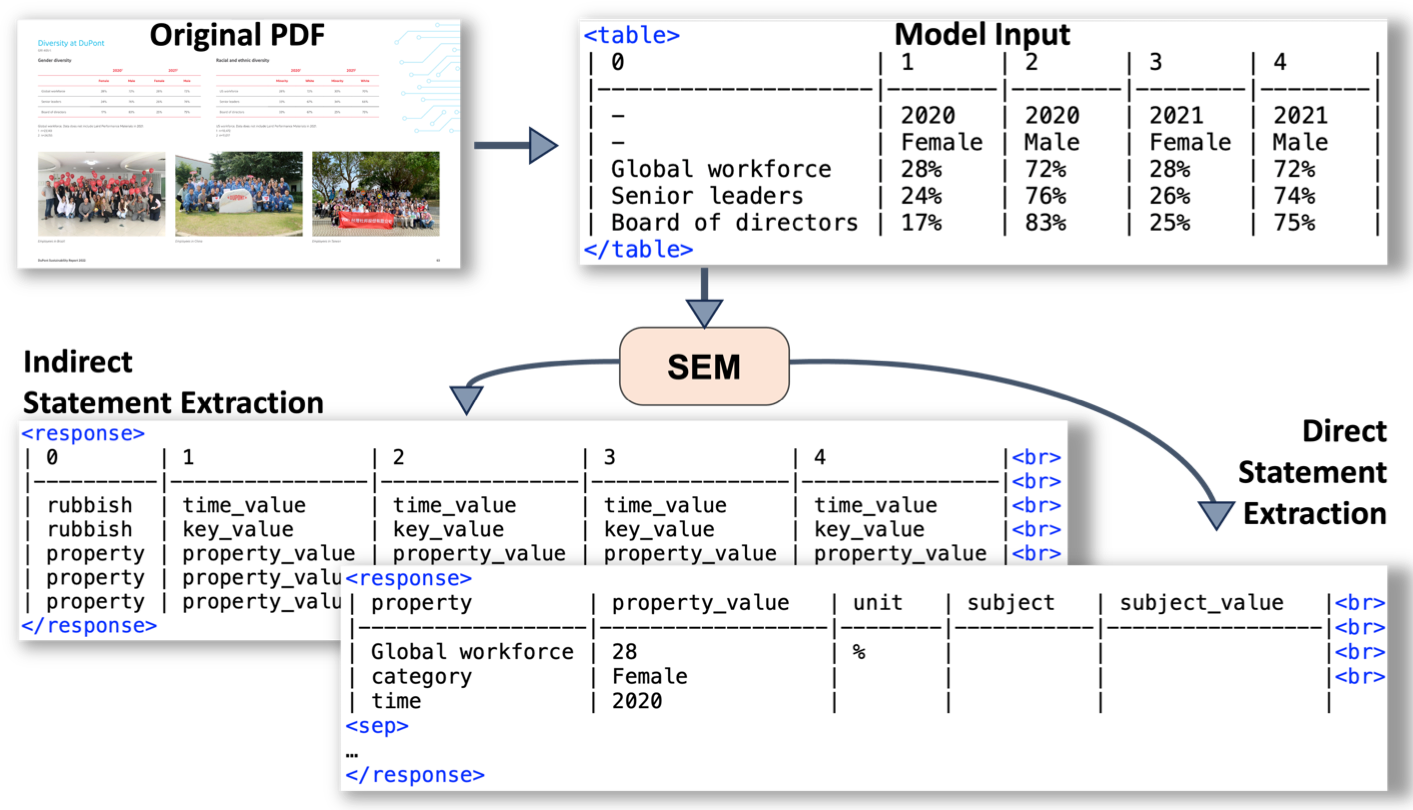 They introduced a method called Statements that translates tables into a tree structure for extracting quantitative facts. They fine-tuned large language models (LLMs) on this new task, creating a dataset called SemTabNet.
They introduced a method called Statements that translates tables into a tree structure for extracting quantitative facts. They fine-tuned large language models (LLMs) on this new task, creating a dataset called SemTabNet.
Results
The best model achieved 82% similarity between the generated statements and the ground truth, significantly outperforming baselines that scored around 21%. This approach was applied to over 2,700 ESG tables, enabling large-scale data analysis.