This year, I attended ACL 2024 in Bangkok. In this series of posts, I’ll share my personal highlights from the conference, focusing primarily on papers and ideas with practical applications.
Prompt Engineering a Prompt Engineer
Motivation
Recent studies indicate that LLMs can be meta-prompted to perform automatic prompt engineering, but their potential is limited due to insufficient guidance for complex reasoning in the meta-prompt.
Method
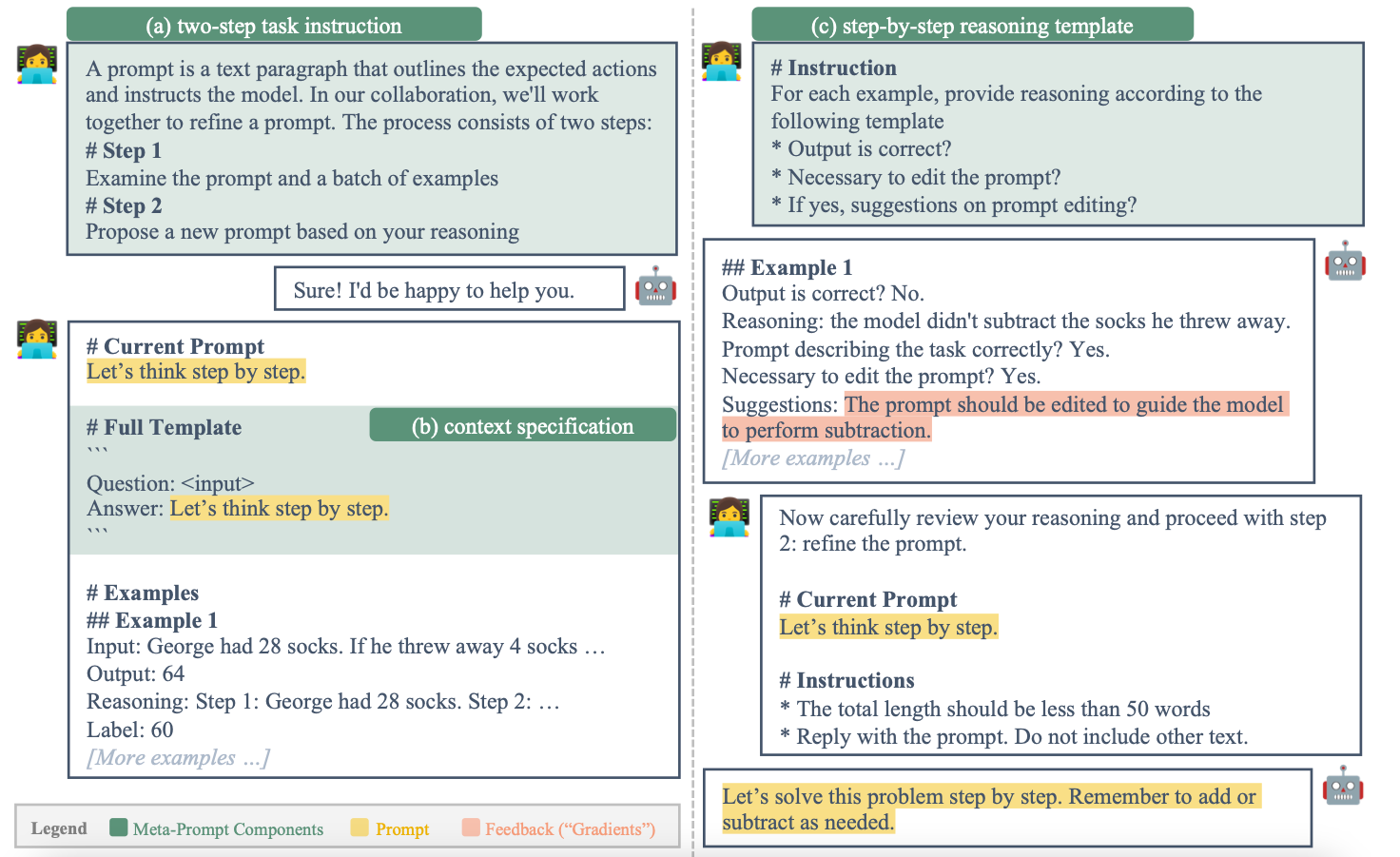 They propose a method consisting of 3 components:
They propose a method consisting of 3 components:
- (a) Two-step Task Description.
- (b) Context Specification.
- (c) Step-by-step Reasoning Template.
Results
Following the proposed method could enhance the prompt boosting the resulting performance.
Controlled Text Generation for Black-box Language Models via Score-based Progressive Editor
Motivation
Existing methods to control text generation are inapplicable to black-box models or suffer a trade-off between control and fluency.
Method
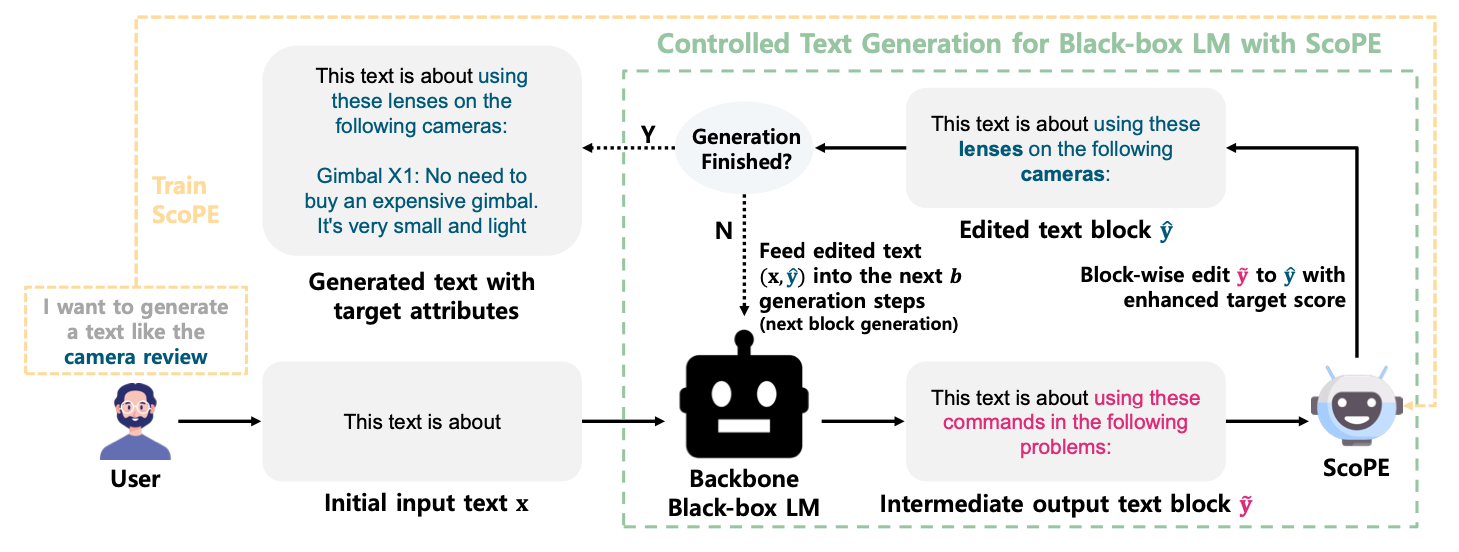 ScoPE is the fine-tuned RoBERTa model, that is trained for text editing. They propose a new approach to control text generation that modifies given text context at the token level during the generation process of a backbone language model and guides subsequent text to naturally include the target attributes.
ScoPE is the fine-tuned RoBERTa model, that is trained for text editing. They propose a new approach to control text generation that modifies given text context at the token level during the generation process of a backbone language model and guides subsequent text to naturally include the target attributes.
Since the method works on a generated text, you could setup any black-box LLM as your backbone LM.
During the inference, their model serves as an agent, that is guiding the LLM enhancing the resulting output after several iterations of editing.
Results
Although, the approach looks promising, the authors were focused on relatively small LLMs, such as GPT3.5, davinci-002, babbage-002. However, there is an additional test with LLAMA2-7B, showing that the method could be beneficial to the larger models as well. But because of the rapidly increasing costs, the method could be considered more as a theoretical.
Referral Augmentation for Zero-Shot Information Retrieval
Motivation
Searching for relevant documents, that provides additional context to the task is the foundation for many information retrieval tasks.
Method
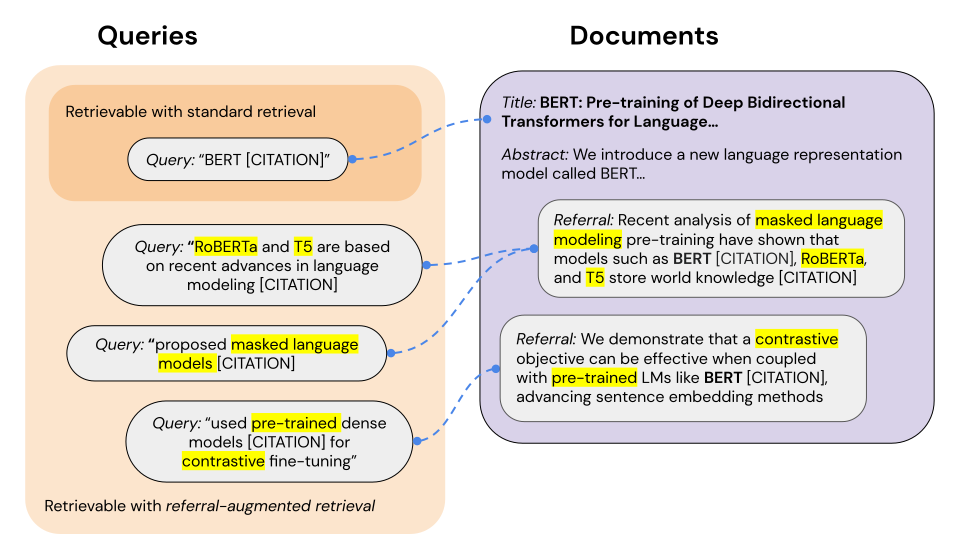 They propose a technique that concatenates document indices with referrals from other documents that cite or link to the given document.
They propose a technique that concatenates document indices with referrals from other documents that cite or link to the given document.
Results
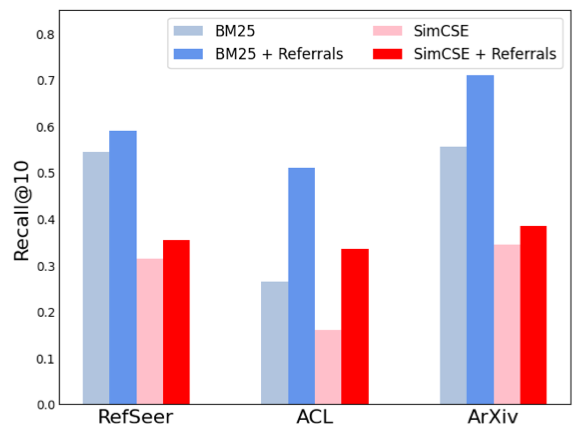 The authors show that including referrals could be beneficial in the information retrieval tasks. However, the referrals are not always available.
The authors show that including referrals could be beneficial in the information retrieval tasks. However, the referrals are not always available.
On LLMs-Driven Synthetic Data Generation, Curation, and Evaluation: A Survey
Motivation
LLMs provide a data-centric solution to reduce limitations of real-world data with synthetic data generation.
Method
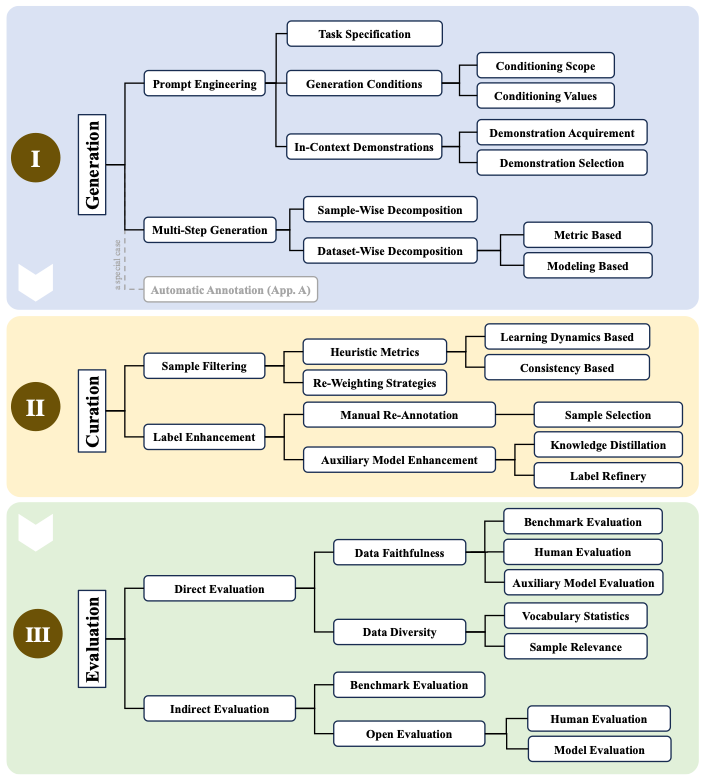 The authors provide an overview of existing models and methods for synthetic data generation, curation and evaluation.
The authors provide an overview of existing models and methods for synthetic data generation, curation and evaluation.
Results
The proposed workflows identify gaps in existing research and outline directions for future research.
Synergistic Interplay between Search and Large Language Models for Information Retrieval
Motivation
Information retrieval (IR) plays a crucial role in locating relevant resources from vast amounts of data.
Method
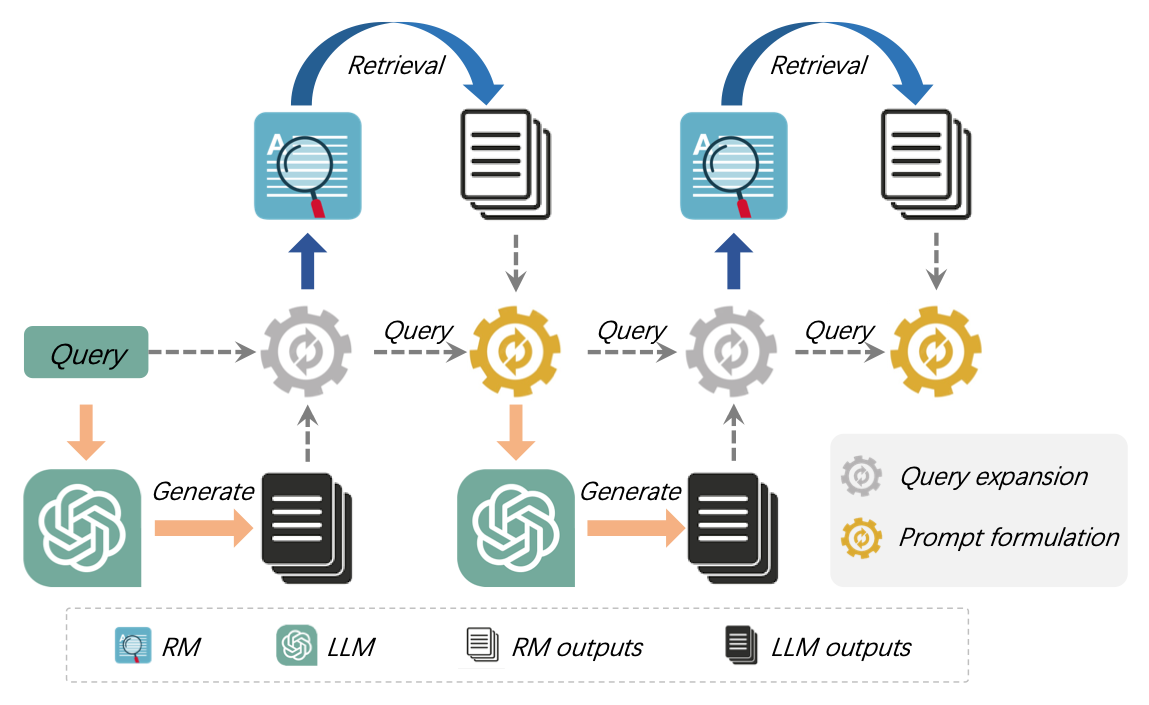 The authors introduce a framework that refines information by combining the strengths of both LLMs and retrieval models (RMs).
The authors introduce a framework that refines information by combining the strengths of both LLMs and retrieval models (RMs).
In each iteration, the RM and LLM components improve the query by using insights from previous iterations. LLMs enhance knowledge collection, while RMs focus on document retrieval. Specifically, the RM refines the query using LLM-generated knowledge to improve document retrieval, and the LLM refines the original query using documents retrieved by the RM to generate more relevant knowledge. This iterative process can be repeated multiple times for further refinement.
Results
The proposed framework improves the performance of large-scale retrieval benchmarks on web searches and low-resource retrieval tasks.
Is Table Retrieval a Solved Problem? Exploring Join-Aware Multi-Table Retrieval
Motivation
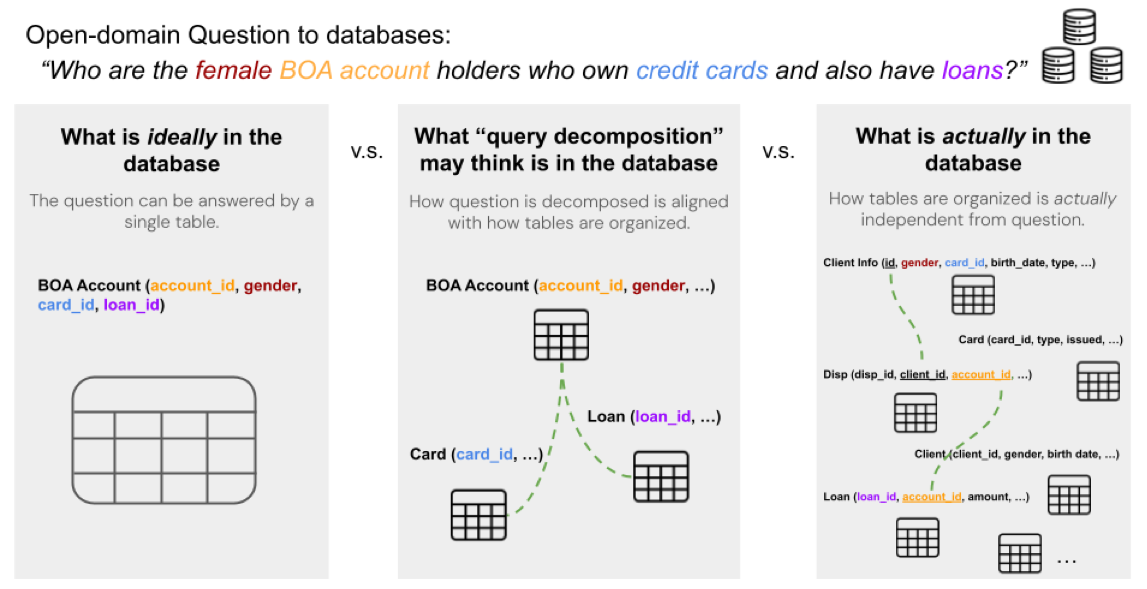 Existing methods for retrieving relevant tables are not sufficient as many questions require retrieving multiple tables and joining them through a join plan that cannot be inferred from the user query directly.
Existing methods for retrieving relevant tables are not sufficient as many questions require retrieving multiple tables and joining them through a join plan that cannot be inferred from the user query directly.
Method
The authors introduce a new re-ranking method to improve table retrieval for user queries. First, the question is broken down using LLMs. Each table is then evaluated for relevance, followed by an assessment of related tables. Finally, the relevant tables are joined to extract all relevant information.
Results
The proposed method outperforms the state-of-the-art methods for table retrieval by up to 9.3% in F1 score and for end-to-end QA by up 5.4% in accuracy.
Learning Relational Decomposition of Queries for Question Answering from Tables
Motivation
Existing approaches to Table Question-Answering focus on generating answers directly from inputs, but there are limitations when executing numerical operations.
Method
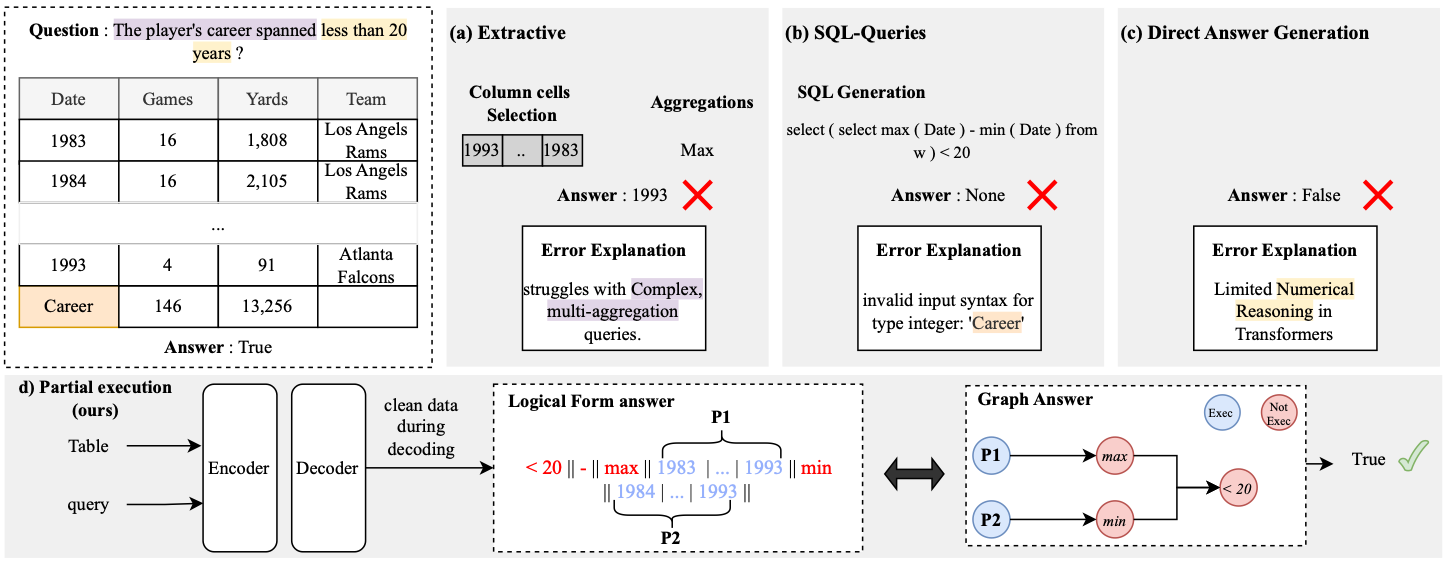 The authors translate a user query into a restricted subset of SQL-like algebraic operations and use them to generate a query.
The authors translate a user query into a restricted subset of SQL-like algebraic operations and use them to generate a query.
Results
The proposed methods bridge the gap between semantic parsing and direct answering methods and offer valuable insights into which types of operations should be predicted by a generative architecture and which should be executed by an external algorithm.
VerifiNER: Verification-augmented NER via Knowledge-grounded Reasoning with Large Language Models
Motivation
Recent approaches in domain-specific named entity recognition (NER) have shown remarkable advances, but they still lack faithfulness, producing erroneous predictions.
Method
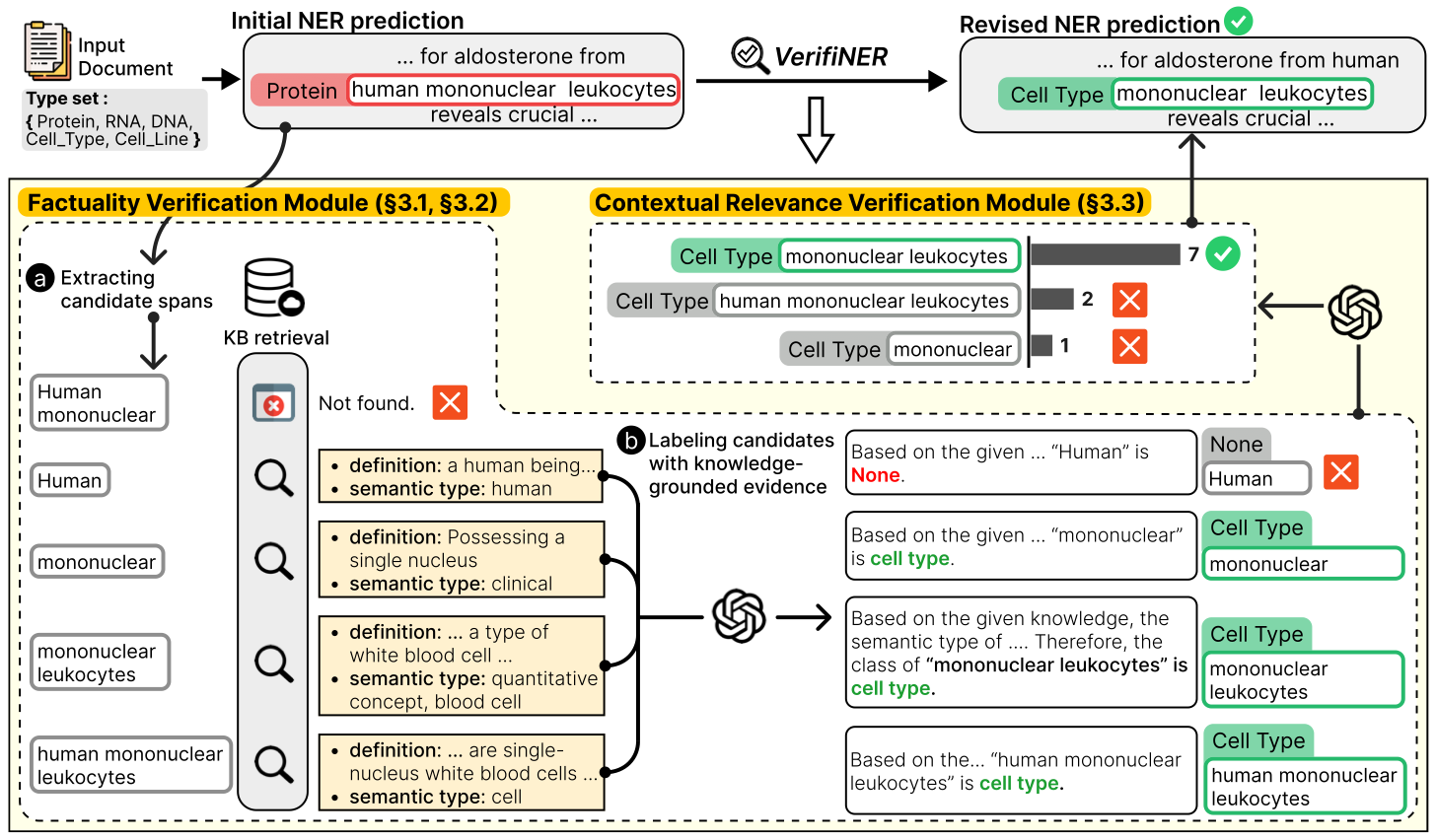 They propose a framework that revises errors from existing NER methods using knowledge to produce more faithful predictions.
They propose a framework that revises errors from existing NER methods using knowledge to produce more faithful predictions.
The first step is to (a) extract all relevant candidate spans from the knowledge base (KB). Then (b) using retrieved knowledge, factuality of type is verified by generating knowledge-grounded evidence. Lastly, the voting is performed to select a candidate that is the most contextually relevant, with the help of the reasoning ability of LLMs.
Results
The proposed framework can validate errors from existing models as a model-agnostic approach.
Choose Your Transformer: Improved Transferability Estimation of Transformer Models on Classification Tasks
Motivation
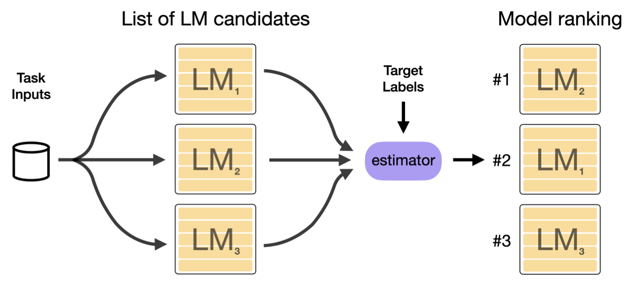 Selecting the right Transformer for a specific down-stream task is challenging. It’s computationally inefficient fine-tuning many models for selecting the best. The authors propose a method to simplify the selection and make it more efficient.
Selecting the right Transformer for a specific down-stream task is challenging. It’s computationally inefficient fine-tuning many models for selecting the best. The authors propose a method to simplify the selection and make it more efficient.
Method
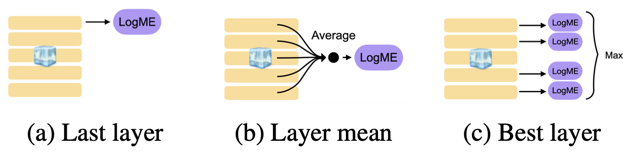 The authors use linear probing, kNN, H-Score and LogME as the estimators to evaluate the potential performance on the downstream tasks without the need to fine-tune each model. They also found that strategy of averaging the layer representation improves the Pearson correlation coefficient between the true model ranks and the estimate.
The authors use linear probing, kNN, H-Score and LogME as the estimators to evaluate the potential performance on the downstream tasks without the need to fine-tune each model. They also found that strategy of averaging the layer representation improves the Pearson correlation coefficient between the true model ranks and the estimate.
Results
The averaging stratecy improves the correlation from 0.58 to 0.86 for LogME and from 0.65 to 0.88 for H-score.
Uncovering Limitations of Large Language Models in Information Seeking from Tables
Motivation
Existing benchmarks for Table Information Seeking (TabIS) are lacking in reliable evaluation.
Method
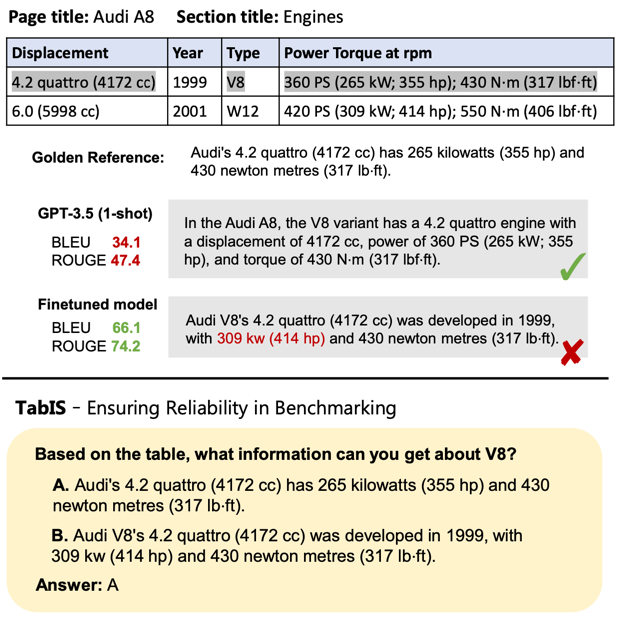 The authors propose a benchmark to evaluate the table information seeking abilities of LLMs. They use a single-choice question format instead of a text-based evaluation on generated text, like BLEU and ROUGE.
The authors propose a benchmark to evaluate the table information seeking abilities of LLMs. They use a single-choice question format instead of a text-based evaluation on generated text, like BLEU and ROUGE.
Results
Experiments on 12 LLMs show that TabIS is a significant challenge, with GPT-4-turbo showing only slight success. LLMs struggle with understanding table structures and maintaining performance against misleading tables, leading to suboptimal results.