DarkBERT: A Language Model for the Dark Side of the Internet
Motivation
Most of pretrained models are trained on the “Surface Web” data, i.e., the content that is readily available and indexed in common search engines such as Google. Therefore the application of these models is limited in cybersecurity and “underground” domain.
Method
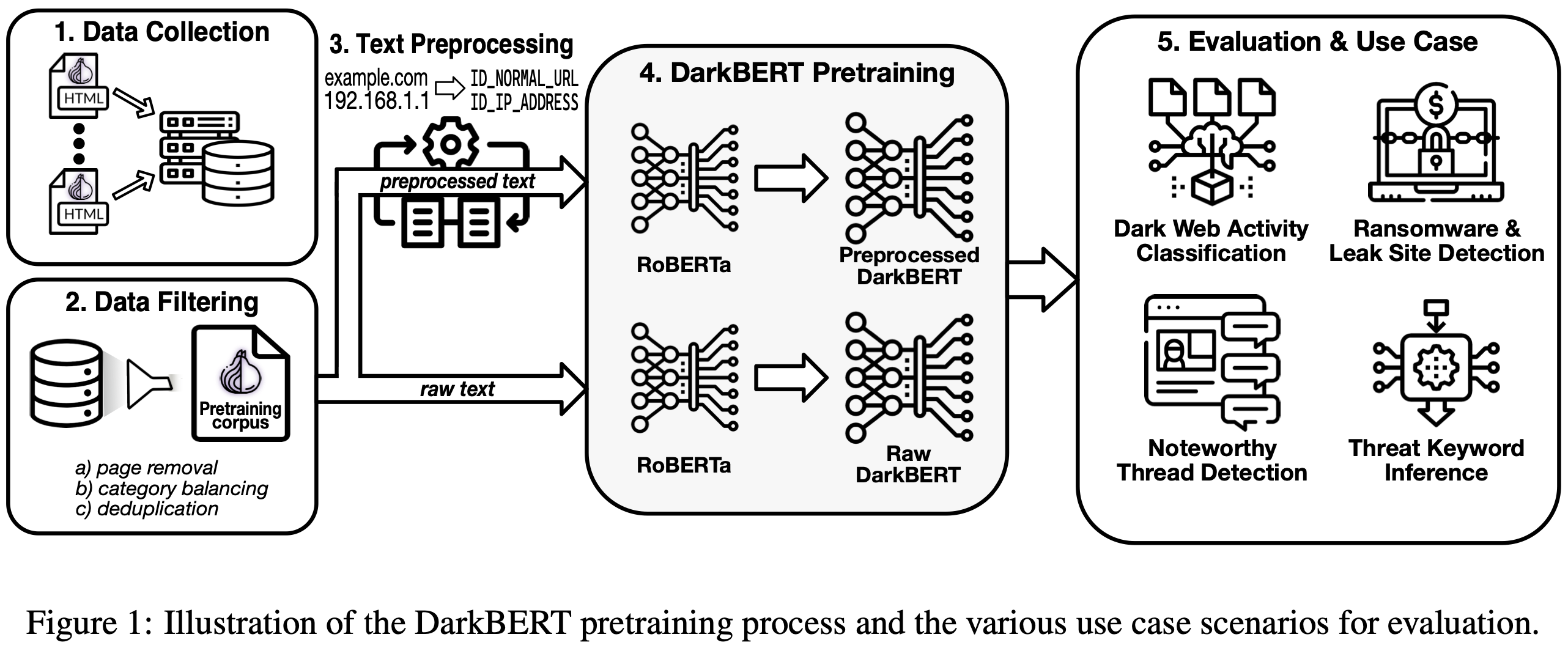 The authors collected a new dataset by crawling Tor network. Then they classified the data using CoDA dataset, removed duplicates and balanced by the categories.
The authors collected a new dataset by crawling Tor network. Then they classified the data using CoDA dataset, removed duplicates and balanced by the categories.
Results
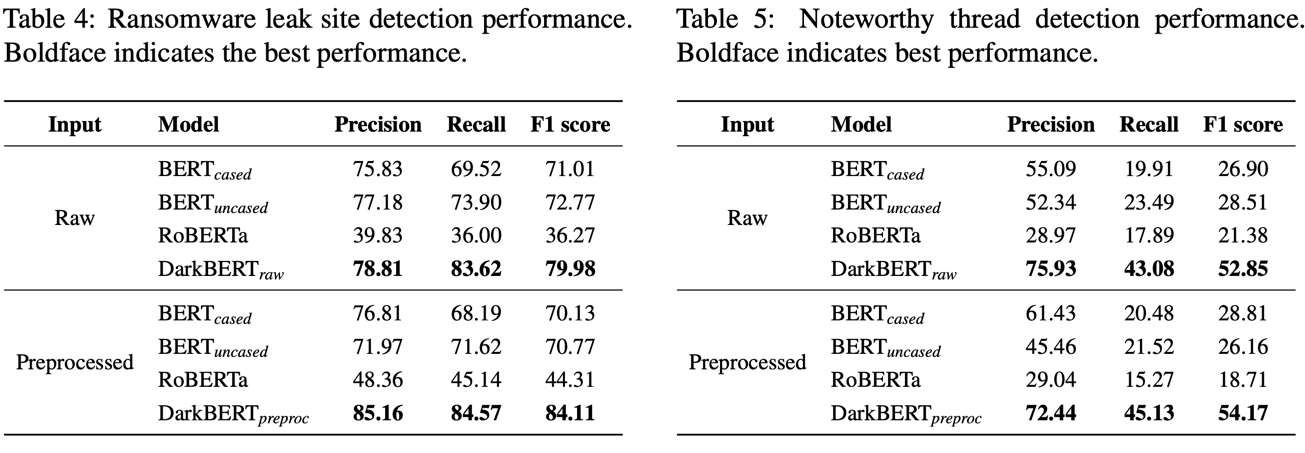 The pretrained model outperforms vanilla BERT models on the “dark” domain of tasks.
The pretrained model outperforms vanilla BERT models on the “dark” domain of tasks.
There’re many application of the model, e.g., activity classification, phishing & ransomware site detection, noteworthy thread detection and threat keyword inference
The model is available on HuggingFace. The use-case data is available upon request.
LENS: A Learnable Evaluation Metric for Text Simplification
Motivation
 There are no solid metric for text simplification task. Most of generic metrics, such as BLEU, BERTScore and specific metrics like SARI correlates with human judgement very poorly. The authors introduce a learnable metric, that demonstrates high correlation with the human scoring.
There are no solid metric for text simplification task. Most of generic metrics, such as BLEU, BERTScore and specific metrics like SARI correlates with human judgement very poorly. The authors introduce a learnable metric, that demonstrates high correlation with the human scoring.
Method
The authors fine-tuned RoBERTa model on their own dataset (SimpEval_past) and then prepare a new benchmark for evaluation (SimpEval2022) text simplification.
Results
The new method shows higher correlation with human judgement not only on their own benchmark, but also on foreign benchmarks. The data as well as the code is available here.
WebIE: Faithful and Robust Information Extraction on the Web
Motivation
Existing Information Enxtraction (IE) datasets mostly based on Wikipedia and not applicable to general web domain where text is noisy and not containing fact triples. Generative models trained on those datasets tend to hallucinate and produce a high rate of false positive results.
Method
The authors present WebIE, entity-linked multilingual IE dataset collected from C4 dataset. Part of the dataset is manually annotated and include a negative examples to better reflect the data on the web.
Results
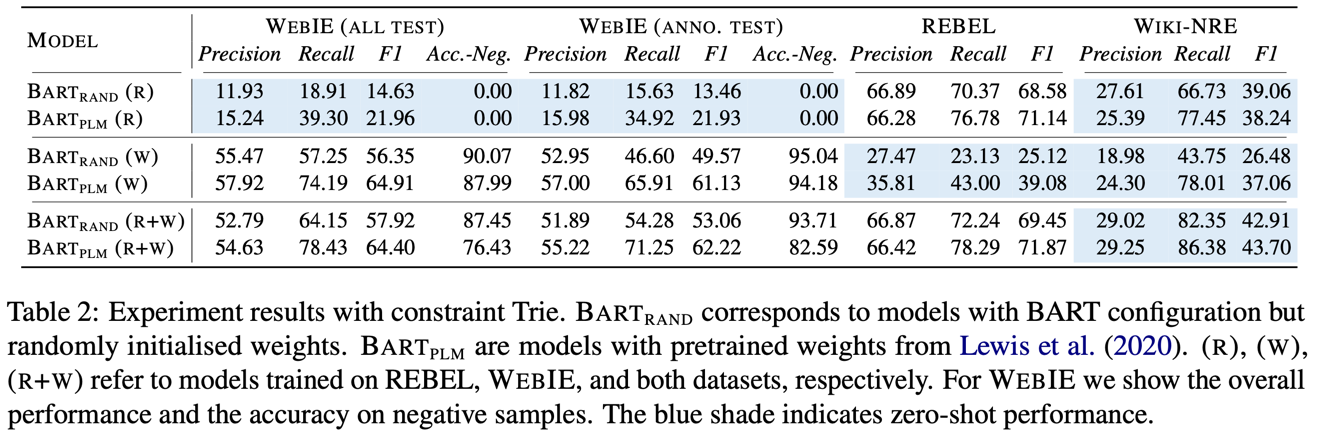
Models trained on WebIE are more generalisable:
- Models trained only on Wikipedia-domain IE datasets leads to 0% accuracy on negative examples
- Models trained on WebIE show promising zero-shot performance on Wikipedia-domain IE datasets
- Models trained on both datasets show best results
UniSumm and SummZoo: Unified Model and Diverse Benchmark for Few-Shot Summarization
Motivation
High annotation costs motivate the research of few-shot summarization, which aims to build specific summarization scenario using very few ground-truth data. However, development of few-shot summarization research is limited from less satisfying summarization models and miscellaneous evaluation benchmark.
Method
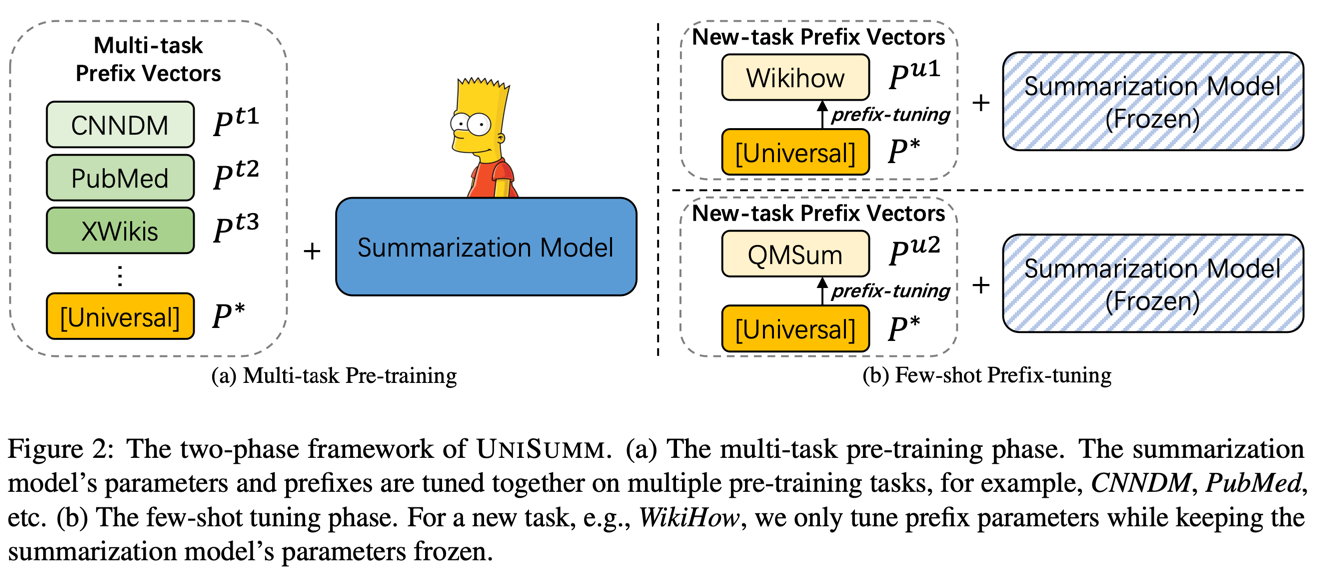
UniSumm, a model that re-uses existing data and can be easily adapted to diverse tasks.
The model is trained using the following steps:
- Pre-train BART model on various summarization datasets. During pre-training the model is divided into 2 parts: prefix and summarization model. Both parts are trained together. During the training, task specific prefix could be replaced with a universal prefix with 15% chance.
- Then the summarization model is frozen and only prefixes are tuned in a few-shot setting. Universal prefix is used in the new prefix initialization. Up to 100 samples are chosen to fine-tune the prefix.
SummZoo, a diverse benchmark consisting of 8 existing summarization tasks.
Results
Results show that the method outperforms other BART models on most of the summarization benchmarks. The authors also try to compare UniSumm with GPT3.5 in few-shot setting, but for some reason, they use only 1-shot for GPT3.5 and 10 and 100-shot for UniSumm, which is completely unfair.
Faking Fake News for Real Fake News Detection: Propaganda-Loaded Training Data Generation
Motivation
Previous work often use synthetic data s the training data for fake news detection as human-crafted fake news are hard to collect.
Method
The authors propose a new method of generating fake news, that better correlates with human-generated articles. They found that most of human-written fake articles contain only 1-2 incorrect sentences and around 33% of text contains propaganda.
The approach consists of the following steps:
- Identify a salient sentence in the article;
- Replace the sentence with generated coherent text, that looks plausible;
- Ensure that the generated information cannot be entailed by the original masked-out sentence; otherwise, the generated texts will not be disinformative.
Results
The authors release the PropaNews dataset, that was generated using the method described above.
Distill or Annotate? Cost-Efficient Fine-Tuning of Compact Models
Motivation
Having a fixed budged and a small annotated data is very common in the development. Then how to build a compact model in a cost-efficient way?
Method
There’re 2 strategies:
- Annotate more data (annotation cost) to directly train a small model;
- Train a larger model, then distill into a small model (computational cost).
Results
- In general, data annotation might not be the best practical solution in light of cost-efficiency; Scale up, then distill.
- For the best performance, however, data annotation is essential despite its inefficiency;
- Synthetic data generation using GPT2.5 could be cost-efficient compared to humans, but still limited.
Parallel Context Windows for Large Language Models
Motivation
LLMs have limited context window size, i.e., some tasks, like text summarization, cannot fit the whole text into context window. Moreover, the existing solutions often require some specific architecture and do not apply to off-the-shelf LLMs.
Method
Proposed method wraps existing model and changes the decoder attention window. 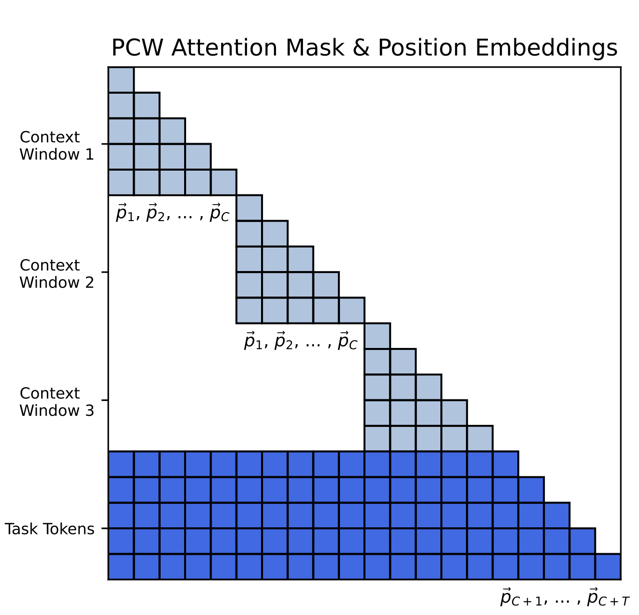
The method could be utilized in few-shot tasks. E.g., you provide several examples of text classification or information extraction, then for the last example you provide just an input, the model should process the data in the same manner as for the samples. 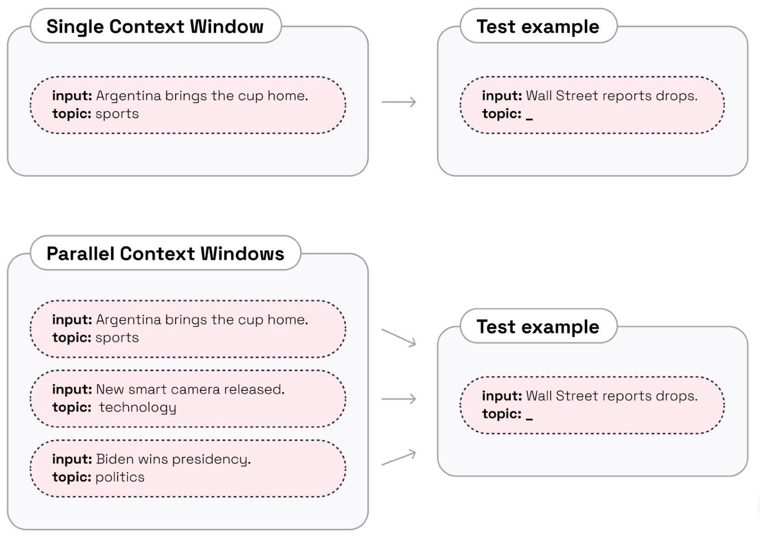
Results
Parallel context windows allows to save some memory and fit more examples into few-shot setting. As a result, improve accuracy in some tasks.